In the United States, the number of people diagnosed with leukemia has decreased over several years. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the overall survival rate for people with leukemia is 65 percent. Although this number is encouraging, it cannot predict your outcome. Therefore, you should work with your medical team to determine your outlook.
Table of Contents
Treatment options for leukemia
There are several treatment options for leukemia, depending on several factors. These include the age and overall health of the patient and whether or not the disease has spread to other parts of the body. One of the most common treatments for leukemia is chemotherapy, which uses powerful drugs to destroy cancer cells. These drugs may be administered through injections or taken in pill form.
New drugs are being developed to fight leukemia and improve the effectiveness of current drugs. For instance, a large clinical trial showed that adding chemotherapy drugs to the standard therapy increased the survival rate of patients with T-cell ALL. In addition, many other drugs are being tested to make standard therapies more effective. Venetoclax is one such drug and has been approved for use in older patients with some forms of leukemia. It is also being tested in children.
Symptoms of leukemia
Several symptoms can be found in children with leukemia. The child may appear pale and tired. Their breathing may also become rapid to compensate for their blood’s decreased oxygen-carrying capacity. A child with leukemia may also have tiny red spots on their skin caused by bleeding blood vessels. Children who have leukemia may also experience repeated infections. In addition, bone and joint pain may occur.
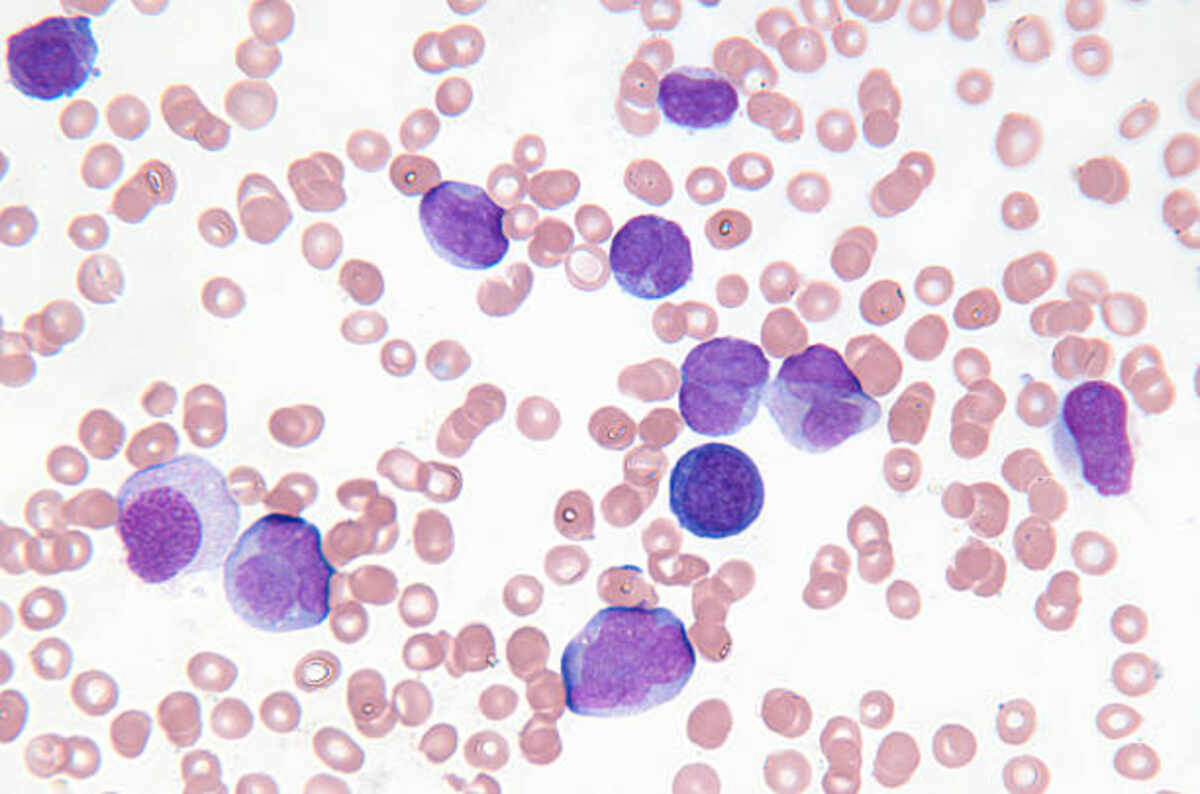
A doctor can diagnose leukemia using blood and bone marrow tests. They may also use immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry to identify cancer cells. Additionally, they may do a chromosome test. Other diagnostic tools include X-rays, ultrasounds, and genetic studies. Another test used to determine the presence of leukemia cells is a lymph node biopsy.
Causes
Leukemia is a severe blood disease that affects both children and adults. The causes are complex and are largely unknown. However, scientists have identified several risk factors associated with an increased risk of leukemia. They include genetic factors, environmental factors, and lifestyle factors. Some risk factors are easily avoidable, while others cannot be avoided entirely.
Leukemia is a blood disease caused by the abnormal development of white blood cells in the bone marrow. These cells are characterized by abnormal chromosomes that interfere with normal cell division. This leads to uncontrolled cell division, resulting in cancerous cells. Depending on its severity and course, the condition is classified as either acute or chronic. Acute leukemia develops quickly, while chronic leukemia advances gradually. It is possible to get multiple types of leukemia.
Tests to diagnose leukemia
Several standard tests diagnose leukemia, including a blood test and a bone marrow biopsy. These tests help doctors determine the type of leukemia and the best treatment options. Symptoms of the disease can be detected through a physical examination, but the only way to know if you have the disease is through tests.
The blood tests used to diagnose leukemia are often the first step in a treatment plan. Some tests are more specific than others. A complete blood count will show the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and lymphocytes.
Treatment options
There are various treatment options for leukemia, including chemotherapy, bone marrow transplant, stem cell therapy, and targeted therapies. These therapies target the genes and surface proteins of cancer cells and help stop the growth of the disease. Some leukemia patients will also undergo bone marrow transplants, usually combined with chemotherapy and total body irradiation. During treatment, doctors will discuss the potential benefits and risks of the various treatment options.
Some types of leukemia do not require immediate treatment. Physicians may recommend a “watch and wait” approach in these cases. This involves periodic blood tests and regular doctor appointments. Unfortunately, this can last for years.